Understanding Natural and Conventional Skincare
Understanding the differences between natural and conventional skincare is vital to making informed choices. Each type has distinct characteristics, benefits, and environmental impacts.
Definition of Natural Skincare
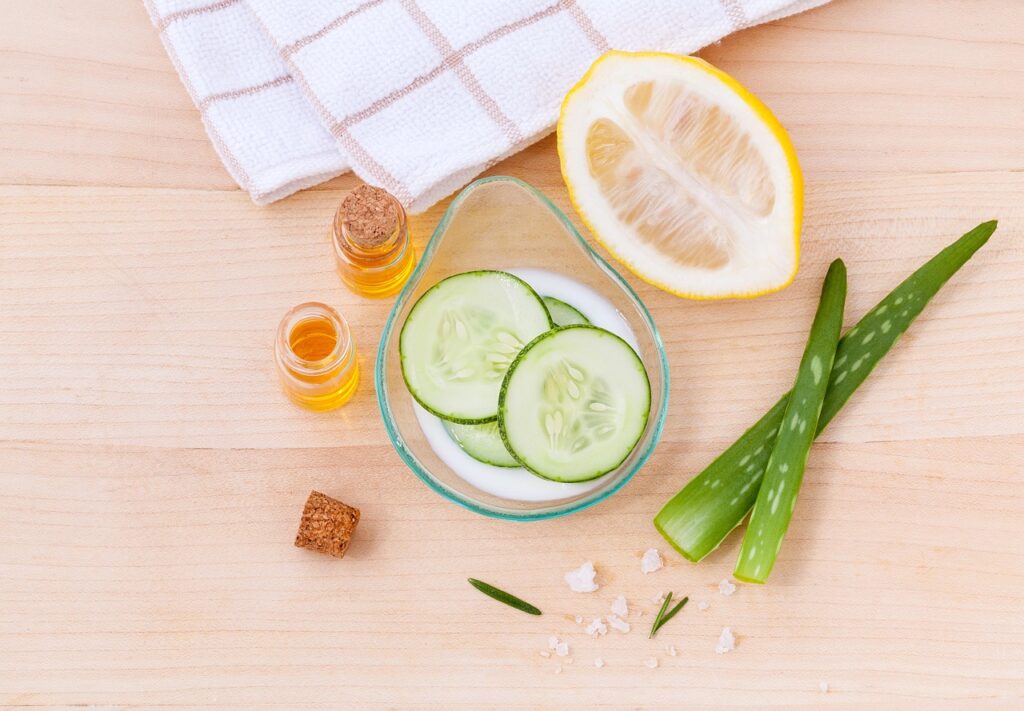
Natural skincare refers to products formulated with ingredients derived from plants, minerals, and other naturally occurring substances. These products typically avoid synthetic chemicals, preservatives, and artificial fragrances. Many natural skincare brands prioritize sustainable sourcing, biodegradable packaging, and ethical practices. For example, they often use ingredients like aloe vera, coconut oil, and shea butter.
Definition of Conventional Skincare
Conventional skincare includes products that often contain synthetic chemicals, artificial fragrances, and preservatives. These products can include ingredients like parabens, sulfates, and phthalates. While conventional skincare is effective and widely available, it may involve environmentally harmful practices. Non-recyclable packaging and non-biodegradable ingredients contribute to waste and pollution. Many mainstream brands use these ingredients to ensure longer shelf life and consistent performance.
Ingredients and Their Origins
Understanding the origins of ingredients in skincare products illuminates their environmental impact. Let’s delve into common ingredients used in natural and conventional skincare.
Common Ingredients in Natural Skincare
Natural skincare products feature eco-friendly components. For example:
- Aloe Vera: Derived from the aloe plant, it soothes and hydrates skin naturally.
- Shea Butter: Extracted from the nuts of the shea tree, it provides deep moisturizing properties.
- Coconut Oil: Sourced from coconut palm trees, it acts as a natural moisturizer and antibacterial agent.
- Jojoba Oil: Obtained from the jojoba plant, it mimics skin’s natural oils and contributes to hydration.
- Chamomile: Extracted from daisy-like flowers, it calms and reduces inflammation.
These ingredients typically have minimal processing and lower environmental impact.
Common Ingredients in Conventional Skincare
Conventional skincare often relies on synthetic chemicals. Key examples include:
- Parabens: Synthetic preservatives used to prolong shelf life, often sourced from petrochemicals.
- Sulfates: Detergents like sodium lauryl sulfate, which create foaming effects, derived from petroleum.
- Phthalates: Plasticizers found in fragrances, contributing to their lasting power.
- Silicones: Used for smooth texture, often derived from non-renewable fossil fuels.
- Synthetic Fragrances: Complex chemical compounds that provide scent, typically petroleum-based.
These ingredients can contribute to pollution due to their non-biodegradable nature.
Sourcing and Sustainability
The sourcing of ingredients greatly impacts sustainability. Natural skincare emphasizes sustainable practices:
- Ethical Harvesting: Ingredients like shea butter and aloe vera are often harvested using community-centered and environmentally-friendly methods.
- Fair Trade Practices: Many natural ingredients are obtained through fair trade, ensuring equitable wages and sustainable farming.
- Minimal Processing: Natural ingredients undergo minimal processing, reducing energy consumption and waste output.
In contrast, conventional skincare ingredients often involve:
- Petrochemical Extraction: Many synthetic ingredients derive from petroleum, involving intensive drilling and extraction processes.
- High Energy Production: Manufacturing synthetic chemicals requires significant energy use, contributing to carbon emissions.
- Non-renewable Resources: Many components in conventional skincare rely on fossil fuels, which are finite and environmentally harmful.
Choosing products with sustainable sourcing can reduce the environmental footprint of your skincare routine.
Production Processes
Natural and conventional skincare products differ significantly in their production processes. Each method impacts the environment in unique ways.
Natural Skincare Production Methods
Natural skincare production emphasizes minimal processing. Manufacturers extract ingredients like coconut oil and jojoba oil using cold-press or steam-distillation methods. These techniques require less energy than synthetic production. Additionally, natural skincare companies often source ingredients from ethical suppliers who prioritize sustainable harvesting. By maintaining low-impact extraction methods, natural skincare minimizes environmental damage and supports biodiversity conservation.
Conventional Skincare Production Methods
Conventional skincare production involves complex chemical synthesis. Ingredients such as parabens, sulfates, and artificial fragrances are created using petrochemicals. The synthesis process is energy-intensive, often involving high-temperature reactions and utilizing non-renewable resources. Furthermore, the production of synthetic chemicals results in significant waste, including hazardous by-products. This not only contributes to pollution but also poses disposal challenges. Conventional methods thus have a larger carbon footprint compared to their natural counterparts.
Energy Consumption and Waste
Energy consumption in skincare production varies greatly between natural and conventional methods. Natural skincare uses less energy due to simpler extraction processes. For instance, cold-pressing essential oils consumes minimal energy compared to synthesizing artificial compounds. Conventional production, on the other hand, often entails energy-heavy chemical reactions.
Waste generation also differs. Natural skincare typically produces biodegradable waste. In contrast, conventional skincare leads to non-biodegradable waste, including plastic microbeads and synthetic polymers. This waste persists in the environment, contaminating water sources and harming wildlife. Focusing on energy-efficient and waste-reducing production methods can mitigate the environmental impact of skincare products.
Packaging and Waste Management
Packaging choices greatly affect the environmental impact of skincare products. Different approaches to packaging result in varying levels of waste and recyclability.
Eco-friendly Packaging Options
Eco-friendly packaging prioritizes minimal environmental impact. Brands use materials like recycled paper, biodegradable plastics, and glass. For example, some companies package their skincare in glass jars and use paper-based labels to reduce plastic use. Packaging designed for reuse or refills also helps cut waste, thus contributing to a circular economy.
Conventional Packaging Practices
Conventional skincare often relies on non-recyclable packaging. Products usually come in plastic containers or tubes, which add to landfill waste if not recycled properly. Many conventional brands package their products in mixed-material containers, complicating the recycling process. Non-biodegradable packaging increases the long-term environmental burden.
Recycling and Disposal
Recycling and proper disposal mitigate packaging waste. Eco-conscious brands provide recycling instructions and take-back programs. Some companies even partner with recycling initiatives to ensure packaging gets processed correctly. Consumers should check local recycling guidelines to dispose of containers properly. In contrast, conventional brands might not prioritize these practices, leading to increased landfill waste.
By choosing products with sustainable packaging and following proper disposal methods, skincare routines can be environmentally responsible.
Consumer Impact and Awareness
Consumer choices have a significant impact on the environment. Awareness and preferences drive changes in the skincare industry, pushing brands toward sustainable practices.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumers increasingly prefer eco-friendly skincare options. Sustainable brands offering natural ingredients like coconut oil, shea butter, and aloe vera are gaining popularity. Surveys from industry reports indicate a rising demand for products without synthetic chemicals, reflecting concerns over health and environmental hazards. More consumers now seek brands with transparent sourcing methods and minimal packaging.
Awareness and Education
Education plays a crucial role in shaping consumer behavior. Awareness campaigns highlight the environmental impact of conventional skincare products. Programs by environmental organizations and eco-conscious brands inform buyers about harmful ingredients and sustainable alternatives. Consumer knowledge influences purchasing decisions, emphasizing the importance of choosing natural and biodegradable products.


 Jewelldane Fultz is a skincare specialist and beauty enthusiast who has spent years studying the science behind healthy skin. Known for her expertise in formulating effective skincare routines, Jewelldane emphasizes simplicity and consistency to help people achieve long-lasting results. Her in-depth knowledge of skincare ingredients makes her a trusted source for anyone looking to enhance their natural glow.
Jewelldane Fultz is a skincare specialist and beauty enthusiast who has spent years studying the science behind healthy skin. Known for her expertise in formulating effective skincare routines, Jewelldane emphasizes simplicity and consistency to help people achieve long-lasting results. Her in-depth knowledge of skincare ingredients makes her a trusted source for anyone looking to enhance their natural glow.
